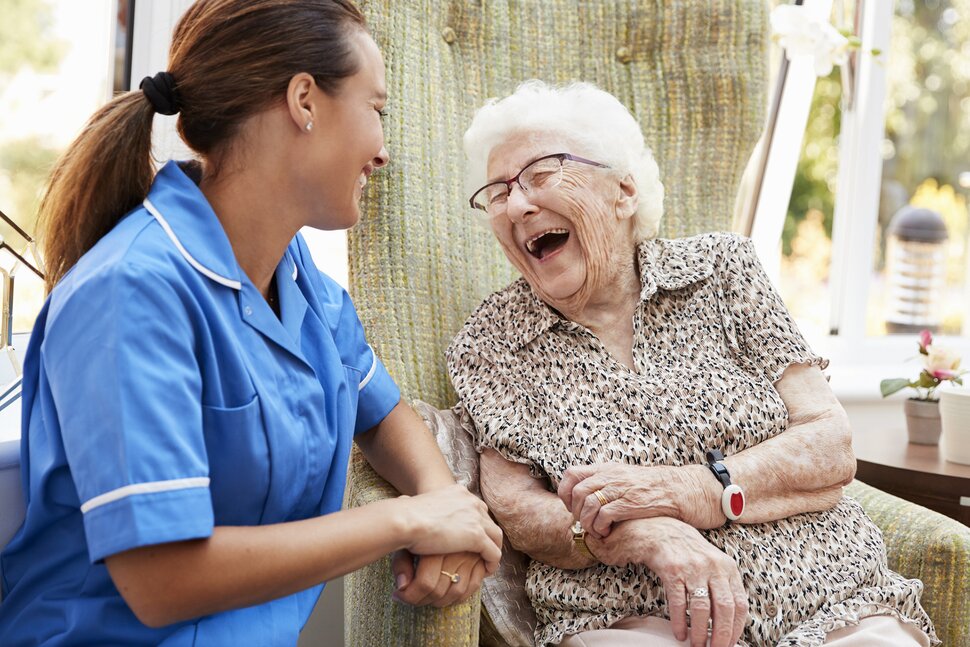

Home-base care refers to the delivery of healthcare services within a person's home. It involves providing support, assistance, and care to individuals who need help with daily activities, medical management, or personal care, ensuring they remain in their own environment.
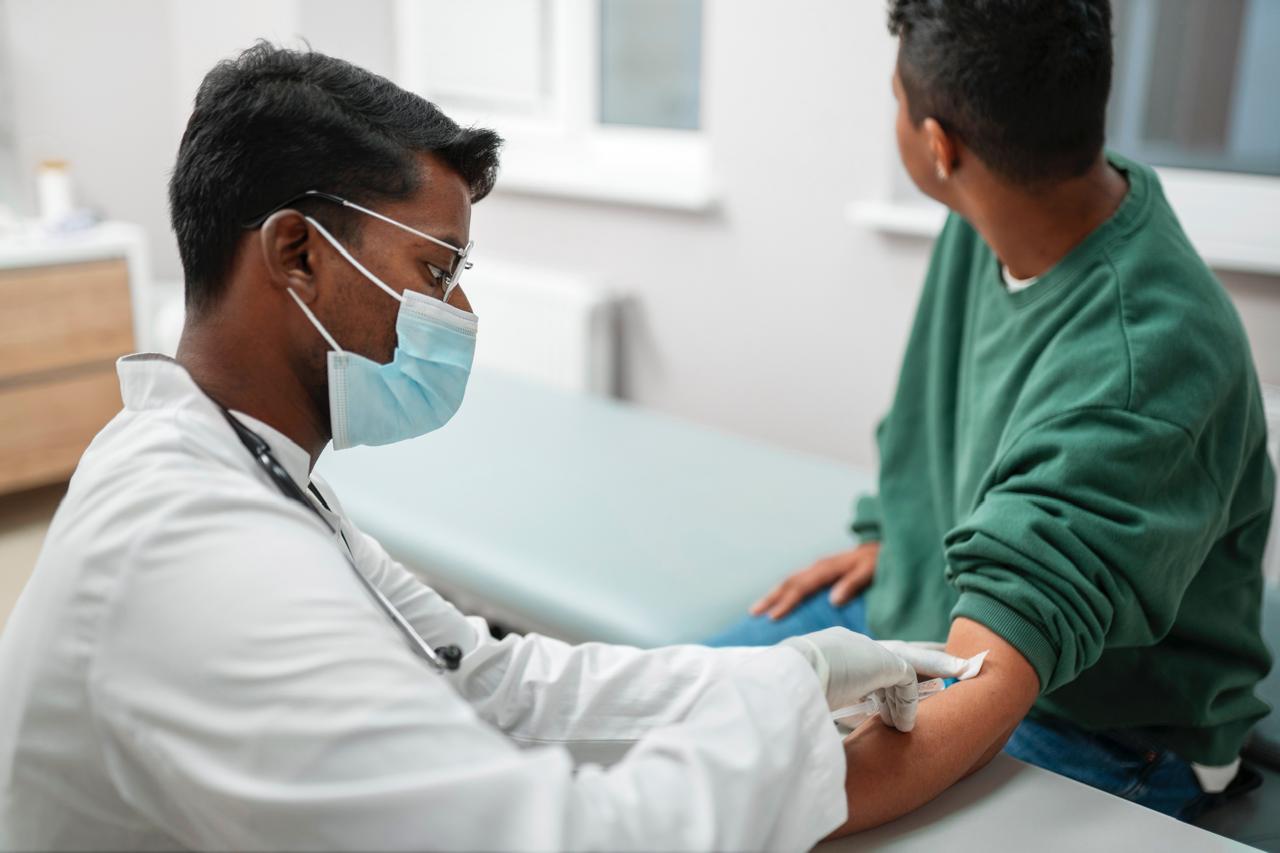
Health Care Assistant course equips individuals with the knowledge and skills to provide direct patient care under the supervision of a nurse or other healthcare professional. The course covers basic anatomy, hygiene, communication, and patient care, including areas such as elderly care and first aid.
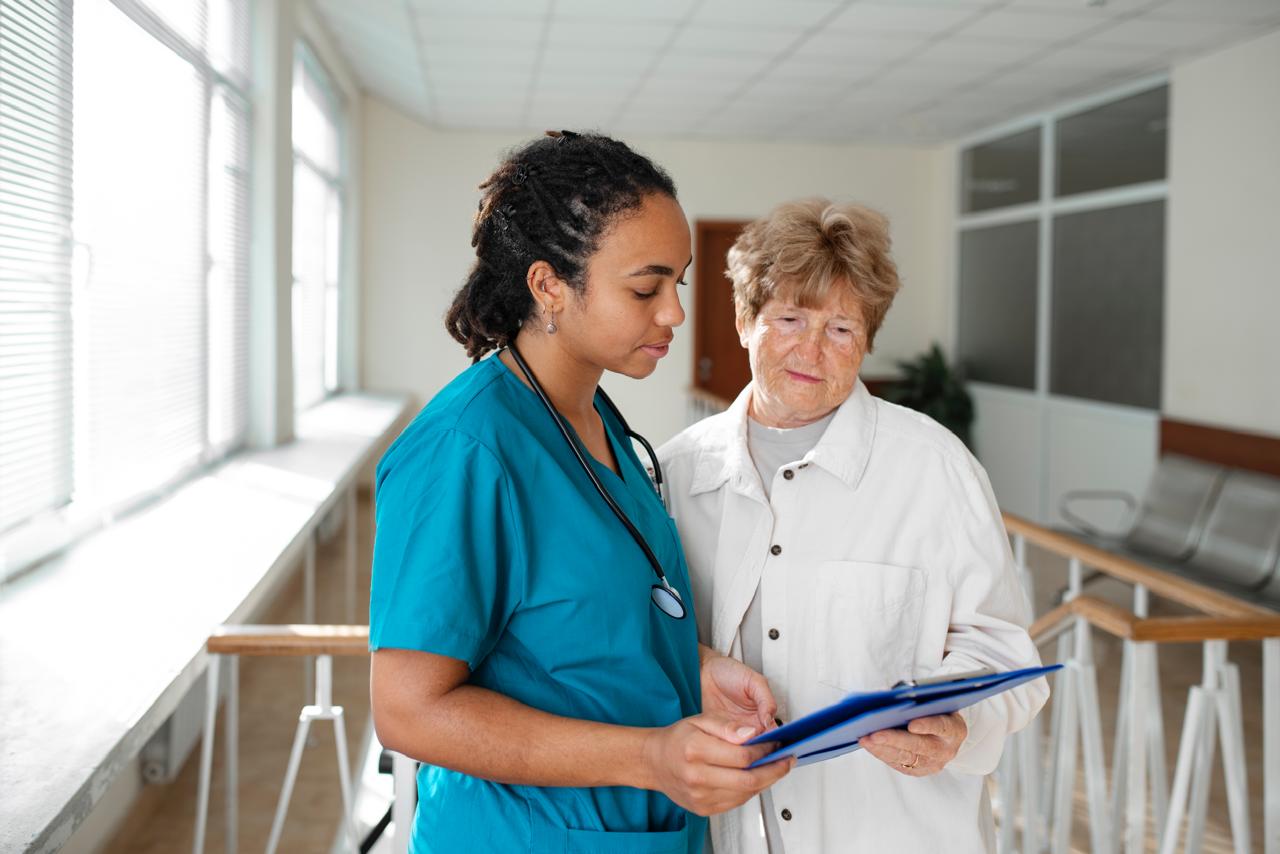

Palliative care is specialized medical care focused on improving the quality of life for individuals with serious illnesses, providing relief from symptoms, pain, and stress. It is not limited to end-of-life care and can be provided alongside curative treatments and reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses.
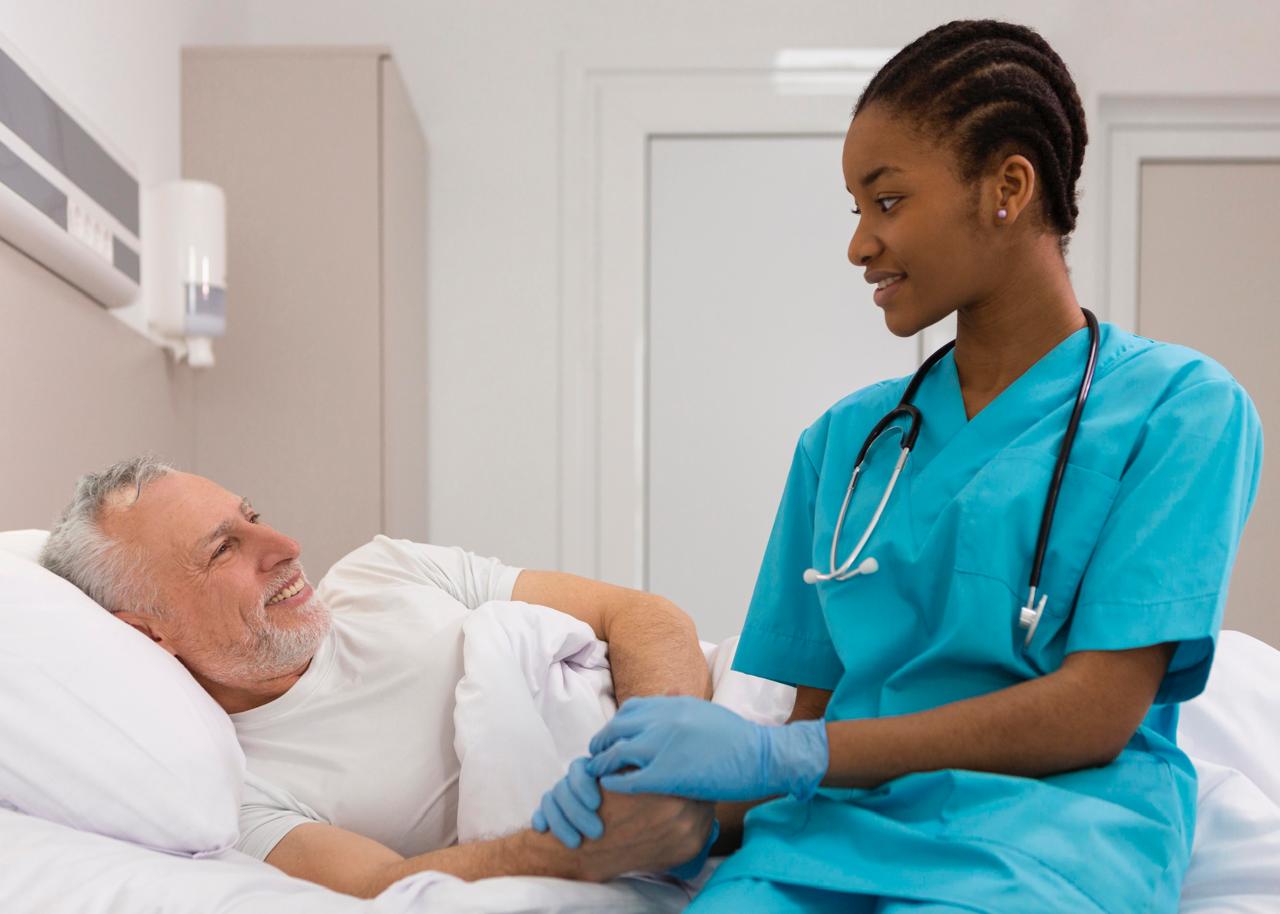

Alzheimer's and dementia care encompass a range of services designed to support individuals living with these conditions and their caregivers, focusing on maintaining quality of life, safety, and independence. This includes managing symptoms, providing emotional support, and adapting the environment to meet the individual's needs.
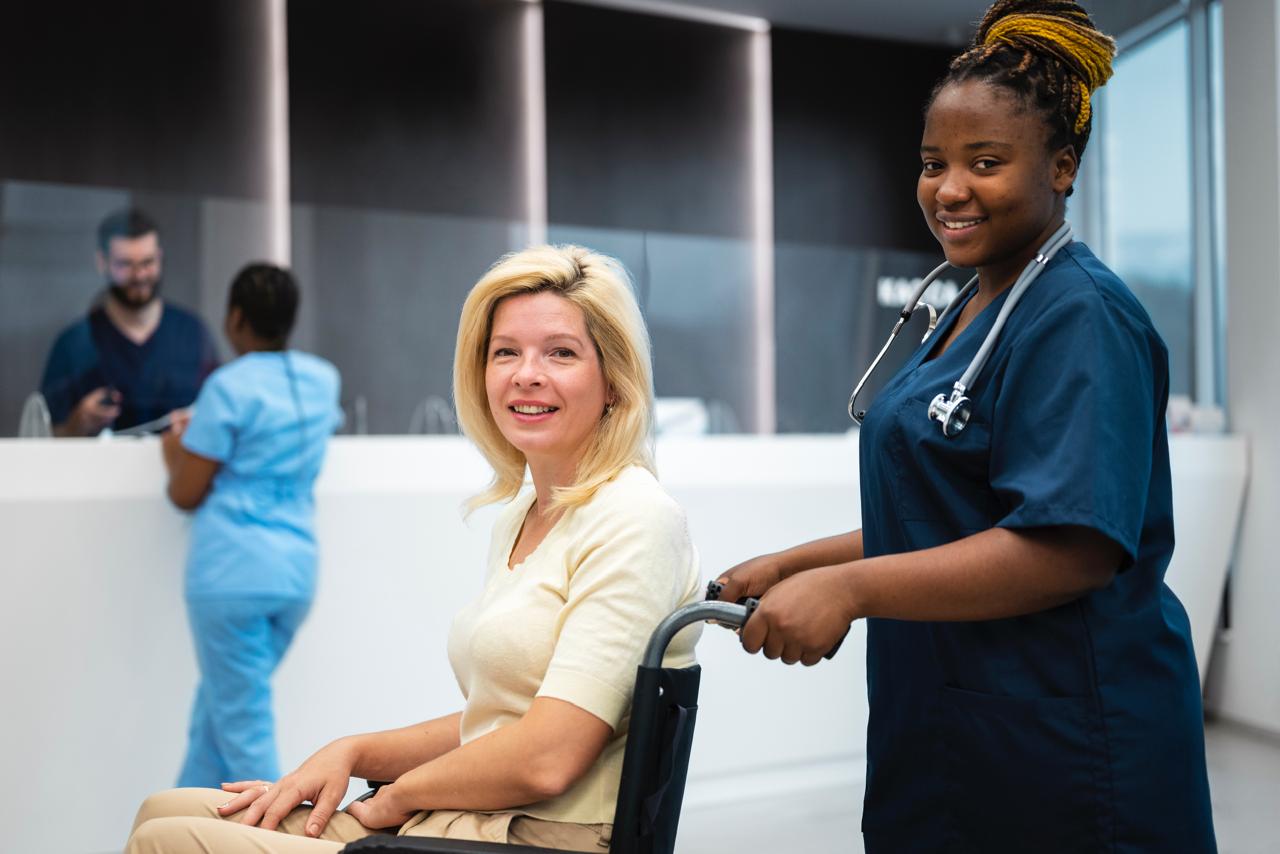

A Patient Care Practitioner is a healthcare professional who provides direct patient care, often as a first point of contact for individuals with health issues. They assess patients, diagnose illnesses, prescribe treatments, and provide direct care, potentially referring patients for further treatment as needed. This role can encompass various settings, including clinics, hospitals, and community-based healthcare services.
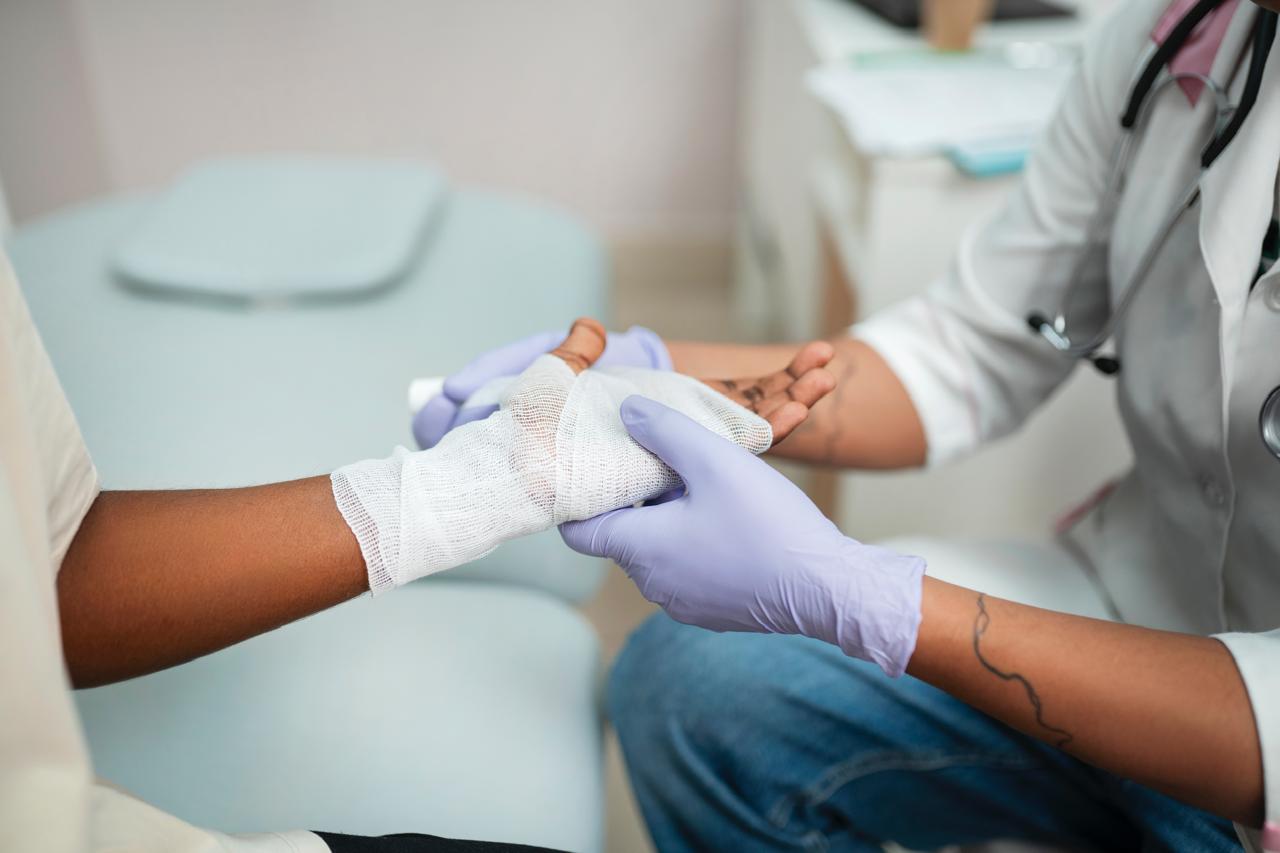
Wound Care Management is a comprehensive process focused on optimizing the healing of wounds, whether they are acute or chronic. It involves cleaning and disinfecting wounds, promoting tissue growth, managing pain, preventing infection, and selecting appropriate dressings to create an optimal healing environment. Effective wound care also considers the underlying causes of the wound and addresses factors that may impede healing.

A HAST (HIV/AIDS/STI and TB Management) course provides healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills to effectively manage HIV, AIDS, Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), and Tuberculosis (TB). Cover topics such as diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and the management of opportunistic infections and comorbidities. The goal is to improve patient care.

HIV/AIDS counseling with rapid testing is a process that combines HIV testing with counseling services, both before and after the test, to help individuals understand their HIV status and make informed decisions about their health. Rapid testing provides results quickly, often within minutes, allowing for immediate post-test counseling and potential linkage to care.